'82er ![]() - Info's
- Info's

Jeep CJ
The Jeep CJ models are both a series and a range of small, open-bodied off-road vehicles and compact pickup trucks, built and sold by several successive incarnations of the Jeep automobile marque from 1945 to 1986. The 1945 Willys Jeep was the world's first mass-produced civilian four-wheel drive car. In 1944, Willys-Overland, one of the two main manufacturers of the World War II military Jeep, built the first prototypes for a commercial version – the CJ, short for "civilian Jeep". From then on, all CJ Jeeps consistently had a separate body and frame, rigid live axles with leaf springs both front and rear, a tapering nose design with flared fenders, and a fold-flat windshield, and could be driven without doors. Also, with few exceptions, they had part-time four-wheel drive systems, with the choice of high and low gearing, and open bodies with removable hard or soft tops. After remaining in production through a range of model numbers, and several corporate parents, the Jeep CJ line was officially ended in 1986. More than 1.5 million CJ Jeeps were built, having continued the same basic body style for 45 years since the Jeep first appeared. Widely regarded as "America's workhorse", the CJs have been described as "probably the most successful utility vehicle ever made." American Motors VP Joseph Cappy said the end of "CJ production will signal an end of a very important era in Jeep history." The Jeep CJ-7 was replaced in 1986 by the similar-looking Jeep Wrangler. The Jeep CJ-8 and CJ-10s were succeeded by the Jeep Comanche pickup. |
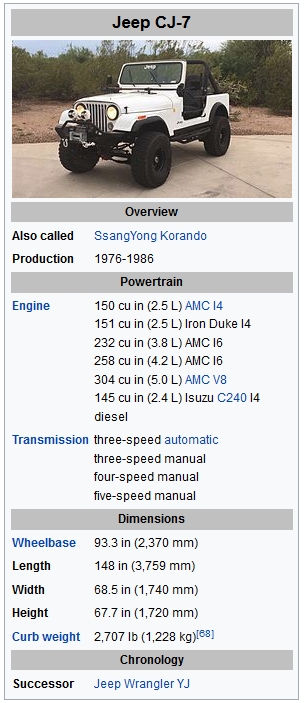 |
The Jeep CJ-7 featured a wheelbase 10 inches longer than that of the CJ-5, with its curved side entry cutouts partially squared up to accommodate hinged doors. The other main difference between CJ-5 and CJ-7 was to the chassis, which consisted of two parallel longitudinal main c-section rails. To help improve vehicle handling and stability, the rear section of the chassis stepped out to allow the springs and shock absorbers to be mounted closer to the outside of the body. It was introduced for the 1976 model year, with 379,299 built during 11 years of production. Transmission options included the standard part-time two-speed transfer case, automatic, and an optional new automatic all-wheel drive system called Quadra-Trac. Other features included an optional molded hardtop, and steel doors. The CJ-7 was also available in Renegade and Laredo models. Distinguished by their different body decals, the Laredo model featured highback leather bucket seats, a tilting steering wheel, and a chrome package that included the bumpers, front grill cover, and side mirrors. An optional Trak-Lok rear differential was available, too. Axle ratio was typically 2.73, with 3.13 as an option (standard in high-altitude regions). The reports of the CJ-7 were different in each type of engine: the 145 cu in (2.4 L) diesel was mated to the 4.10 ratio axle (in both Renegade and Laredo), while the 258 cubic-inch straight six and 150 cubic-inch four-cylinder used 3.73 and AMC V8 304-powered models (produced 1976-1981, which became part of the Golden Eagle version) used the 3.55 ratio axles. |
A diesel-powered version was made in the Ohio factory for export only. The engines were provided by General Motors, the owners of Isuzu Motor Cars. Production of this diesel version was between 1980 and 1982. This model had the Isuzu C240 engine, T176 transmission, and Dana 300 transfer case, although reports of some being produced with the Dana 20 exist. Typically, they had 4.1-ratio, narrow-track axles. From 1976 to 1980, the CJ-7 came equipped with a Dana 20 transfer case, Dana 30 front axle (27- or 31-spline), and a 29-spline AMC 20 rear axle, while later years, Laredo packages added tachometer, chrome bumpers, tow hooks, and interior upgrades including leather seats and clock. In 1980, the Laredo was first fitted with an AMC 20 rear axle until mid-1986, when it was equipped with a Dana 44, and all 1980 and newer CJ-7s came with the Dana 300 transfer case. The Canadian Army took delivery of 195 militarized versions of the CJ-7 in 1985. These were put into service as a stop-gap measure between the retirement of the M38A1 and the introduction of the Bombardier Iltis. They were codified by the Canadian Forces with the Equipment Configuration Code number 121526. The CJ-7 continues to be used in the sport of mud racing, with either the stock body or a fiberglass replica. CJ-7 has been successfully and widely used as a favorite for rock crawling, through simple and complex modification. These last Jeeps produced were also highlighted with a factory dash plaque that read, "Last of a Great Breed - This collectors-edition CJ ends an era that began with the legendary Jeep of World War II". During its 11 years, the CJ-7 had various common trim packages: 1976-1986 Renegade (2.4D L6-2.5-4.2-5.0 AMC 304 V8) 1976-1980 Golden Eagle (5.0 AMC 304 V8) 1980 Golden Hawk (5.0 AMC 304 V8) 1980-1986 Laredo (2.4D-4.2 I6) Jeep also produced two special edition CJ-7 packages: - 1982-1983 Limited (2,500 units were built as a limited-production luxury model; 4.2-L I6 with T5 or automatic transmissions) - 1982 Jamboree Commemorative Edition (630 numbered units built for the 30th anniversary of the Rubicon Trail; 4.2L). with only 630 units produced (560 Topaz Gold Metallic and 70 Olympic White), the CJ-7 Jamboree is the rarest CJ-7 ever built and one of the rarest Jeeps of all time. The Jamboree is in the same production rarity class as the 1971 CJ-5 Renegade-II. It is the most heavily optioned CJ ever built; it was the Rubicon of its day. All units were uniquely numbered via a dash plaque; it is the only AMC Jeep to have been numbered. |